[ad_1]
Price action is at the heart of technical analysis, a simple and effective way to identify trading opportunities. We delved into the three main principles of price movement with examples; trend, support and resistance, and market reaction.
Highlights:
- Price action analysis is an effective way to isolate potential trading opportunities
We look at how to identify trends, support and resistance, and reaction signals for validation
Put it all together and make trading decisionsTechnical analysis encompasses many disciplines, but its foundation is price action. Three key components – trend, price levels (support/resistance) and market reaction can provide actionable signals.
Trend
There are many indicators that identify a trend and its strength, but what really defines a trend from a simple price perspective is whether the market is making higher highs and higher lows (uptrend) or lower lows and lower lows. Highs (downtrend) or do nothing and create a zone like this.
Trends appear on all timeframes, but a general rule of thumb is that higher timeframes take precedence over shorter timeframes. For Forex, for example, using daily and 4 hours is a solid combination to get the full picture.
While the 4-hour chart (short-term) is likely to see an uptrend, the daily chart (long-term) is likely to see a downtrend. In this case, more attention should be paid to the trend on the daily chart, keeping in mind that the short-term trend may eventually reverse in favor of the long-term trend.
Example of an Uptrend
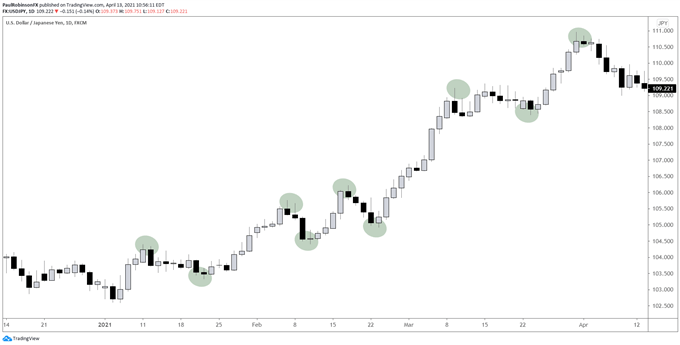
Example of a Downtrend
Support and Resistance
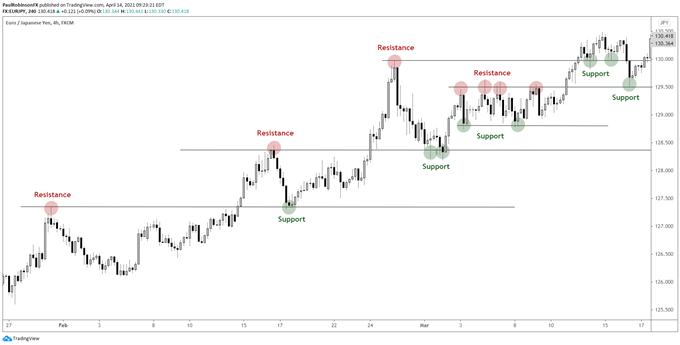
The next important aspect of price action trading is price levels – support and resistance. Support is simply the point at which demand (buyers) holds price support, while resistance is a form of supply (sellers), the point at which the market stops moving higher. There are many ways to identify these levels, such as: B. Fibonacci levels and moving averages, but the focus here is mainly on actual price levels, trend lines, and slopes.
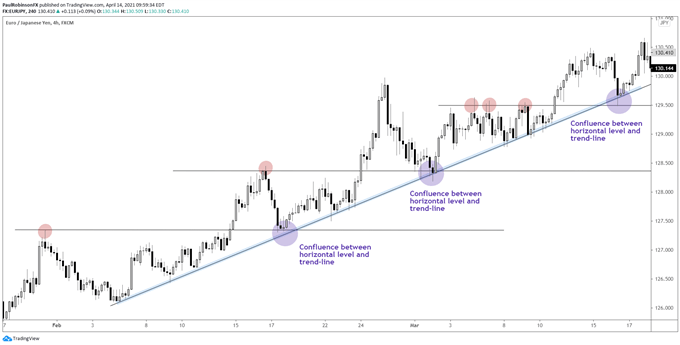
An important note – the confluence between different support and resistance angles makes the level stronger and more reliable. For example, if you have a horizontal price level that intersects a trendline, that is a stronger level.
Example of support and resistance
Example of confluence
Market Reaction (Validation, Invalidation)
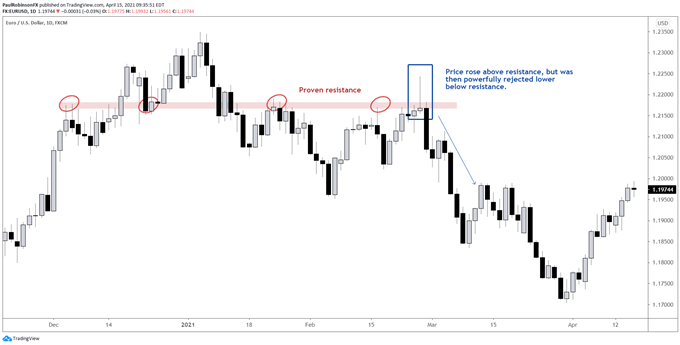
A third aspect to consider in price action trading is how the market reacts to price levels in the context of a trend. Does the behavior the market exhibits confirm or refute what we see on the charts? This is where rubber meets the road and trade decisions can be made.
A good way to measure price action is to use candlestick analysis. The types of candlesticks that show a clear reaction or rejection are reversal candles (also known as “pin” bars, “shooting stars”, “bull hammers”) and other strong candles such as “engulfing bars”.
These candlesticks show rejection away from the support or resistance in question, and a change in momentum suggests the market is willing to engage key levels.
Once a support or resistance reversal occurs, we can use swing lows (bulls) and swing highs (bearers) to determine where to place a stop loss. It is best to place your stop loss after the relevant level to avoid being triggered by small movements above or below the identified level. The target should provide an adequate return relative to the risk taken (a general rule of thumb is a risk-reward ratio of 1:2 or higher). Targets, such as stop losses, should also be based on your analysis, not random numbers determined by how much you want to make.
Example of powerful reversal around resistance
[ad_2]
