[ad_1]
The role of central banks in the forex market
The central bank is primarily responsible for maintaining inflation to promote sustained economic growth, while promoting the overall stability of the financial system. If central banks deem it necessary, they will intervene in financial markets in accordance with the established monetary policy framework. Forex traders seeking to take advantage of the resulting currency movements closely monitor and anticipate the implementation of such policies.
This article focuses on the role of major central banks and how their policies affect the global foreign exchange market.
What is a central bank?
Central banks are independent institutions that countries around the world use to help manage their commercial banking industries, set central bank interest rates, and promote national financial stability.
Central banks intervene in financial markets by:
- Open market operations: Open Market Operations (OMO) describes the process by which governments buy and sell government securities (bonds) on the open market with the aim of expanding or contracting the money supply in the banking system.
- The central bank rate: The central bank interest rate, often called the discount rate or the federal funds rate, is set by the monetary policy committee to increase or decrease economic activity. It may seem counterintuitive, but an overheated economy can lead to inflation, which the central bank tries to keep at moderate levels.
The central bank also acts as the lender of last resort. If the government has a moderate debt-to-GDP ratio and does not raise funds through bond auctions, the central bank can lend money to the government to cover its temporary liquidity shortage.
The central bank’s role as lender of last resort increases investor confidence. Investors are more assured that the government will meet its debt obligations, which helps reduce the cost of government borrowing.
Major central banks
Federal Reserve Bank (United States)
According to the 2016 Triennial Central Bank Survey, the Federal Reserve or “Federal Reserve” controls the world’s most traded currency. The actions of the Fed affect not only the dollar, but other currencies as well, which is why the actions of the banks have received a lot of attention. The Fed’s goals are stable prices, sustainable employment and moderate long-term interest rates.
European Central Bank (European Union)
The European Central Bank (ECB) is different because it is the central bank of all member states of the European Union. The ECB prioritizes preserving the value of the euro and maintaining price stability. The euro is the second most widely circulated currency in the world, thus attracting a lot of attention from foreign exchange traders.
Bank of England
The Bank of England, as the central bank of the United Kingdom, has two goals: monetary stability and financial stability. The UK adopts a two-peak model in regulating the financial industry, with one “peak” being the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and the other being the Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA). The Bank of England regulates financial services in a prudent manner, requiring such companies to have adequate capital and adequate risk controls.
Bank of Japan
The Bank of Japan prioritizes price stability and stable operation of the payment settlement system. The Bank of Japan has been keeping interest rates below zero (negative rates) in a major effort to revive the economy. Negative interest rates allow individuals to borrow money to get paid, but discourage investors from depositing funds because doing so incurs fees.
Central bank responsibilities
Central banks were created to perform the task of serving the public interest. While responsibilities may vary by country, key responsibilities include the following:
1) Achieving and maintaining price stability: Central banks are tasked with protecting the value of their currencies. This is achieved by maintaining moderate levels of inflation in the economy.
2) Promote financial system stability: The central bank conducts a series of stress tests on commercial banks to reduce systemic risks in the financial sector.
3) Promoting balanced and sustainable growth of the economy: Generally speaking, a country can stimulate its economy in two main ways. This is achieved through fiscal policy (government spending) or monetary policy (central bank intervention). When the government runs out of budget, the central bank can still initiate monetary policy to stimulate the economy.
4) Supervision and supervision of financial institutions: The central bank has the responsibility to supervise commercial banks in the public interest.
5) Minimize unemployment: In addition to price stability and sustained growth, central banks may be interested in minimizing unemployment. That’s one of the Fed’s goals.
Central Banks and interest rates
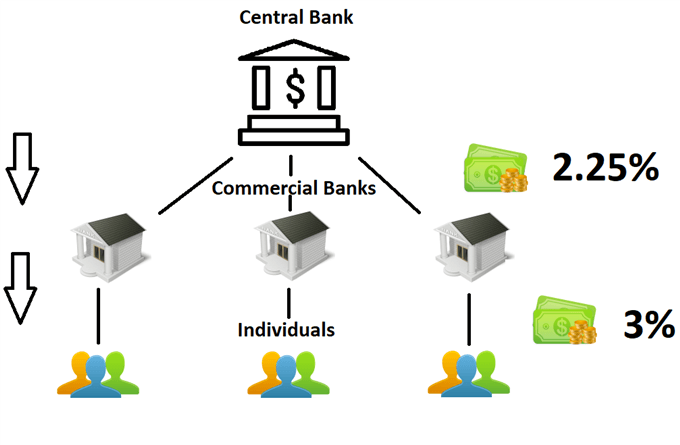
The central bank sets the central bank interest rate, and all other interest rates for individuals on personal loans, home loans, credit cards, etc. are based on this benchmark rate. The central bank rate is the rate charged to commercial banks that wish to borrow overnight from the central bank.
This effect of central bank rates is shown in the graph below, with commercial banks charging higher rates.
Commercial banks must borrow money from the central bank to satisfy a modern form of banking called fractional reserve banking. Banks take deposits and lend, which means they must ensure they have enough cash to meet daily withdrawal needs, while lending depositors’ surplus funds to companies and other investors that need cash. Banks use this process to generate revenue by charging higher rates on loans while paying depositors lower rates.
The central bank sets a specific percentage of all deposits (reserves) that the bank must set aside, and if the bank does not meet this condition, it can borrow money from the central bank at the overnight rate, which is calculated based on the annual interest rate. central bank.
Forex traders pay close attention to central bank interest rates as they can have a significant impact on the foreign exchange market. Institutions and investors tend to follow yields (interest rates), so these rates change.
How central banks impact the forex market
Forex traders often evaluate the language used by central bankers for clues as to whether the central bank is likely to raise or lower interest rates. Statements interpreted as implying an increase/decrease in interest rates are called hawkish/dovish. These subtle clues are known as “forward guidance” and have the potential to drive foreign exchange markets.
Traders who believe the central bank is on the brink of a rate hike cycle will go long to support the currency, while traders who expect the central bank to be dovish will try to short the currency.
Movements in central bank interest rates provide traders with the opportunity to trade through carry trades based on the interest rate differential between the two currencies. Carry traders expect the overnight rate of higher-yielding currencies against lower-yielding currencies.
[ad_2]