[ad_1]
Traders often compare Forex to stocks to determine which market is better to trade. Although they are related, the foreign exchange market and the stock market are very different. The Forex market has unique characteristics that set it apart from other markets and, in the eyes of many, make it more attractive for trading.
When you decide to trade Forex or stocks, it is often necessary to know which trading method is best for you. But understanding the differences and similarities between the stock and forex markets can also allow traders to make informed trading decisions based on factors such as market conditions, liquidity, and volume.
Top 5 Differences between forex and stocks
The table below summarizes a few key differences between the forex market and the stock market:
|
Forex Market |
Stock Market |
|
Large volume- Around $5 Trillion per day |
Less volume – Roughly $200 billion per day |
|
Highly Liquid |
Less liquid |
|
24 Hour Markets |
8 Hour Markets |
|
Minimal or no commissions |
Commissions |
|
Narrow Focus |
Wide Focus |
1) Volume
One of the biggest differences between forex and stocks is the sheer size of the forex market. It is estimated that around $5 trillion is traded in FX every day, with most trades concentrated in a few major currency pairs such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD and AUD/USD. The foreign exchange market’s volume dwarfs the dollar volume of all stock markets around the world, averaging around $200 billion per day.
Such large volumes can bring many benefits to traders. High volume means traders can often fill orders more easily and get closer to the desired price. While all markets are prone to gaps, traders with more liquidity at any price point are more able to enter and exit the market.
2) Liquidity
Markets with high volumes are usually highly liquid. Liquidity results in tighter spreads and lower transaction costs. Compared to stocks, forex major currency pairs usually have extremely low spreads and transaction costs, which is one of the main advantages of forex market trading over stock market trading. Read more about the difference in liquidity between the foreign exchange and stock markets.
3) 24 Hour Markets
Forex is an over-the-counter market, which means it is not conducted through traditional exchanges. The interbank market facilitates transactions. This means that transactions can take place during business hours and trading hours in different countries around the world. Therefore, Forex traders can trade 24 hours a day, 5 days a week. On the other hand, major stock indices trade at different times and are affected by different variables. Visit the major indices pages to learn more about trading these markets, including trading hours information.
4) Minimal or no commission
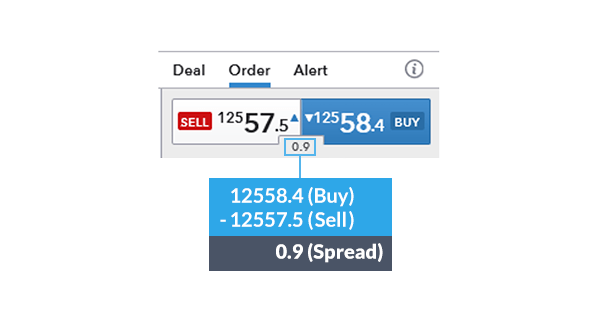
Most forex brokers don’t charge commissions, but earn margin on the spread – the difference between the bid and ask prices. When trading stocks (shares) or futures contracts or major indices like the S&P 500, traders usually have to pay the broker a spread and commission.
Forex spreads are fairly transparent compared to the cost of trading other contracts. Below are the EUR/USD spreads highlighted in the exchange rate for executable trades. Spreads can be used to pre-calculate the cost of your position size prior to execution.
5) Narrow focus vs wide focus
There are eight major currencies that traders can focus on, while there are thousands in the stock space. There are only eight economies to watch, and since forex is traded in pairs, traders will be looking for divergences and converging trends between currencies to match forex pairs to trade. Eight currencies are easier to track than thousands of stocks.
Variables affecting major currencies can be easily monitored using the economic calendar.
Should you trade forex or stocks?
Whether you choose to trade forex or stocks depends greatly on your goals and preferred trading style.
The table below shows different types of trading styles, including the pros and cons of each when trading forex and stocks.
|
Type of Trader |
Definition |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
Forex vs Stocks |
|
Short- Term (Scalping) |
A trading style where the trader looks to open and close trades within minutes, taking advantage of small price movements. |
Traders can focus more on volatility and less on fundamental variables that move the market. |
As a result of placing more trades, beginner traders may lose more money if their strategy isn’t fine-tuned. |
Suited to forex trading due to inexpensive costs of executing positions. Some exchanges require large capital account balances to trade. Most forex brokers only require you to have enough capital to sustain the margin requirements. |
|
Medium-Term |
A trading style where the trader looks to hold positions for one or more days, where the trades are often initiated due to technical reasons. |
Lower capital requirements compared with other styles because a trader is looking for larger moves. |
Trades must be accompanies with analysis which may take time. |
Suited to trading forex and stocks. |
|
Long-Term |
A trading style where a trader looks to hold positions for months or years, often basing decisions on long-term fundamental factors. |
Traders do not have to spend as much time analysing. |
Large capital requirements required to cover volatile movements. |
Suited more to stock trading because the forex market tends to vary in direction more than stocks. |
Forex vs other markets FAQs
How can I transition from forex trading to stock trading?
In order to switch from forex trading to stock trading, you need to understand the basic difference between forex and stocks. If you understand this, forex movements are caused by interest rates and their expected movements. Stocks depend on earnings, balance sheet forecasts, the economies in which they operate, and more. Learn more about how to switch from forex trading to stock trading.
Forex and commodities differ in regulation, leverage and trading restrictions. The foreign exchange market is much less regulated than the commodity market, which is heavily regulated. In terms of leverage, both foreign exchange and commodity markets exist, but are more popular in foreign exchange due to greater liquidity and lower volatility (leverage can magnify losses and gains).
Like stocks, commodities are traded on stock exchanges. Commodity exchanges place upper and lower limits on price fluctuations for commodities, and when these limits are reached, trading may be suspended for a period of time, depending on the product being traded. Forex and stock markets have no borders that can stop trading.
Stay up to date with current currency, commodity and index prices on our Best Prices page. Also, check out our expert trading forecasts for stocks, major currencies USD and EUR, or read our guide to the characteristics of successful traders for top traders who fail
[ad_2]
